Abstract
Purpose
Lentinan is a polysaccharide extracted from Shiitake mushrooms that have been used to improve general health for thousands of years in Asia. Lentinan injection is a clinically approved drug in several countries in Asia. The purpose of this study is to review the structure, preclinical and clinical studies, and molecular mechanisms of lentinan. Most importantly, the clinical effectiveness of lentinan as an adjuvant therapeutic drug in treating patients with lung cancer in China during the past 12 years is analyzed statistically.
Methods
We carried out literature search of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published from 2004 to 2016 based on CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure), VIP (Chongqing VIP Chinese Scientific Journals Database) and Wanfang database, and 38 eligible RCTs of lentinan-associated lung cancer treatment were identified, containing 3,117 patients.
Results
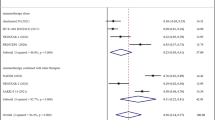
The structure and function relationship and underlying molecular mechanism of lentinan as an immunostimulant has been summarized. The mean value of overall response rate in treating lung cancer was increased from 43.3% of chemotherapy alone to 56.9% of lentinan plus chemotherapy [p < 0.001, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.102–0.170]. Compared with chemotherapy alone, lentinan plus chemotherapy showed more efficacy in treating lung cancer (pooled RR 0.79, 95% CI 0.74–0.85) and no statistical heterogeneity was found among studies (I2 = 11%).
Conclusion
Clinical data presented in the past 12 years shows that lentinan is effective not only in improving quality of life, but also in promoting the efficacy of chemotherapy during lung cancer treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai R (2010) Radiation and chemotherapy combined with lentinan to treat with non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastasis. Hebei Med J 32:2046–2047
Banin Hirata BK, Oda JMM, Losi Guembarovski R et al (2014) Molecular markers for breast cancer: prediction on tumor behavior. Dis Mark 2014:1–12
Bao L, Wang Y, Ma R et al (2015) Apoptosis-inducing effects of lentinan on the proliferation of human bladder cancer T24 cells. Pak J Pharm Sci 28:1595–1600
Barrett SV (2010) Breast cancer. J R Coll Physicians Edinb 40:335–339
Bekkering S, Blok BA, Joosten LA et al (2016) In vitro experimental model of trained innate immunity in human primary monocytes. Clin Vaccine Immunol 23:926–933
Brown GD, Gordon S (2003) Fungal beta-glucans and mammalian immunity. Immunity 19:311–315
Carter P (2001) Improving the efficacy of antibody-based cancer therapies. Nat Rev Cancer 1:118–129
Chai M, Xiao Y (2005) Effect of lentinan in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Med Forum 26:69–70
Chang X, Shao P, Huang X et al (2013) Clinical research on cisplatin combined lentinan in local therapy of malignant pleural effusion. New Med 44:840–842
Chen J, Raymond K (2008) Beta-glucans in the treatment of diabetes and associated cardiovascular risks. Vasc Health Risk Manag 4:1265–1272
Chen J, Seviour R (2007) Medicinal importance of fungal β-(1 → 3), (1 → 6)-glucans. Mycol Res 111:635–652
Chen Q, Peng H, Dong L et al (2016) Activation of the NRF2-ARE signalling pathway by the Lentinula edodes polysaccharose LNT alleviates ROS-mediated cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Int immunopharmacol 36:1–8
Cheng SC, Quintin J, Cramer RA et al (2014) mTOR- and HIF-1α-mediated aerobic glycolysis as metabolic basis for trained immunity. Science 345(6204):1250684
Cheung NK, Modak S, Vickers A et al (2002) Orally administered beta-glucans enhance anti-tumor effects of monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Immunol Immunother CII 51:557–564
Chihara G, Maeda Y, Hamuro J et al (1969) Inhibition of mouse sarcoma 180 by polysaccharides from Lentinus edodes (Berk.) sing. Nature 222:687–688
Clynes RA, Towers TL, Presta LG et al (2000) Inhibitory Fc receptors modulate in vivo cytotoxicity against tumor targets. Nat Med 6:443–446
Dai X (2010) Observation on chemotherapy combined with lentinan to treat metaphase or terminal non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Med Pract 14:73, 77
Dai D (2014) Recent and long-term effect and adverse reaction of lentinan combined with GP chemotherapy in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Mod J Integr Tradit Chin West Med 23:1627–1628
Dai J, Wu W (1998) Regulatory effect of lentinan on immune functions of patients with lung cancer. Cancer Res Prev Treat 25:144–145
Deng M, Wang S, Liu Z (2010) One case of anaphylactic shock induced by lentinan injection. Chin J Drug Appl Monit 07:321–322
Ding N, Huang Z, Zhang Q et al (2012) Observation of clinical effect of lentinan and vinorelbine and cisplatin recombination on patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Anhui Med J 33:681–683
Forman D, Ferlay J (2014) The global and regional burden of cancer. In: Stewart BW, Wild CP (eds) World cancer report 2014. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, p 16
Gordon M, Bihari B, Goosby E et al (1998) A placebo-controlled trial of the immune modulator, lentinan, in HIV-positive patients: a phase I/II trial. J Med 29:305–330
Hamy AS, Belin L, Bonsang-Kitzis H et al (2018) Pathological complete response and prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for HER2-positive breast cancers before and after trastuzumab era: results from a real-life cohort. Br J Cancer 118:e14
Han L, Li J, Liu Y (2012) A clinical observation of lentinan combined with GP regimen in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Her Med 31:1029–1032
He D, Li J, Chen Z (2015) Recent and long-term effect observation of lentinan combined with EP chemotherapy in the treatment of small cell lung cancer. J Huaihai Med 33:598–599
Hirsch FR, Franklin WA, Veve R et al (2002) HER2/neu expression in malignant lung tumors. Semin Oncol 29:51–58
Ina K, Furuta R (2017) Complete response of metastatic gastric cancer to chemoimmunotherapy. Indian J Med Res 146:141
Ina K, Furuta R, Kataoka T et al (2011) Lentinan prolonged survival in patients with gastric cancer receiving S-1-based chemotherapy. World J Clin Oncol 2:339–343
Ina K, Kataoka T, Ando T (2013) The use of lentinan for treating gastric cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 13:681–688
Jiang X, Zhou G (2009) Clinical research of combined lentinan for injection with chemotherapy on advanced non-small cell lung cancer. China Mod Dr 47:74–75
Jiang R, Tan X, Liu W et al (2010) Therapeutic effect of combined lentinan, gemcitabine and cisplatin in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Med J Qilu 25:132–134
Kay NE, LaPlant BR, Pettinger AM et al (2018) Cumulative experience and long term follow-up of pentostatin-based chemoimmunotherapy trials for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Expert Rev Hematol 11:337–349
Kupfahl C, Geginat G, Hof H (2006) Lentinan has a stimulatory effect on innate and adaptive immunity against murine Listeria monocytogenes infection. Int Immunopharmacol 6:686–696
Levine DB (2008) The Hospital for the Ruptured and Crippled: William Bradley Coley, third Surgeon-in-Chief 1925–1933. HSS J 4:1–9
Li X (2001) Progress in anti-tumor drugs. China Pharm 12:429–431
Li Z, Zhu Y, Zhang P et al (2009) Clinical observation on GP chemotherapy combined with lentinan to treat advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Pract Med 25:3480–3482
Li J, Song W, Wang S (2013) 30 cases of advanced non-small cell lung cancer treat with lentinan combined with GP chemotherapy. Guangdong Med J 34:1432–1434
Li C, Zhu T, Lu X (2016) Clinical analysis of the application of lentinus edodes polysaccharides combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of patients with advanced lung cancer. Mod Diagn Treat 27:1614–1616
Liu D, Qian J, Pu M (2003) Research status of anti-tumor effect of lentinan. Edible Fungi 2:6–7
Liu W, Gu J, Qi J et al (2015) Lentinan exerts synergistic apoptotic effects with paclitaxel in A549 cells via activating ROS-TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome. J Cell Mol Med 19:1949–1955
Lu C (2013) Clinical observation on 26 cases of lung cancer with malignant pericardial effusion treated with lentinan and cisplatin. Guiding J Tradit Chin Med Pharm 19:53–54
Lu H, Hong S, Zhang X (2008) Clinical analysis of 63 cases with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with lentinan combined with NP chemotherapy. J XinJiang Med Univ 31:92–93
Lv G, Fan L, Zhang Z et al. (2009) Development of research on lentinan. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis 21:183–188
Ma J (2014) Efficacy of lentinan combined with NP regimen in treatment of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and its effect on immunologic function. Chin J Biochem Pharm 34:154–156
Makanjuola SB, Popoola AO, Oludara MA (2014) Radiation therapy: a major factor in the 5-year survival analysis of women with breast cancer in Lagos. Niger Radiother Oncol 111:321–326
Murphy EA, Davis JM, Carmichael MD (2010) Immune modulating effects of beta-glucan. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 13:656–661
Nishitani Y, Zhang L, Yoshida M et al (2013) Intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of lentinan: influence on IL-8 and TNFR1 expression in intestinal epithelial cells. PLoS One 8:e62441
Novakovic B, Habibi E, Wang SY et al. (2016) β-Glucan reverses the epigenetic state of LPS-induced immunological tolerance. Cell 167(5):1354–1368
Peng X, Fan X, Shi X et al (2008) Influence of lentinan on expression of TLR4, TLR9 of mouse splenic T/B cells. Chin J Clin Pharmacol 24:234–236
Peng J, Zhang X, Chen C et al (2013) Nursing care of 3 cases of allergy caused by intravenous infusion of lentinan. Chin Gen Pract Nurs 11:1512
Peter G, Karoly V, Imre B et al (1988) Effects of lentinan on cytotoxic functions of human lymphocytes. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 10:157–163
Qian J (2010) 34 cases clinical observation of lentinan adjuvant therapy in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Mod Drug Appl 04:114–115
Quintin J (2018) Fungal mediated innate immune memory, what have we learned? Semin Cell Dev Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.05.023
Quintin J, Saeed S, Martens JHA et al (2012) Candida albicans infection affords protection against reinfection via functional reprogramming of monocytes. Cell Host Microbe 12:223–232
Ruthes AC, Smiderle FR, Iacomini M (2016) Mushroom heteropolysaccharides: a review on their sources, structure and biological effects. Carbohyd Polym 136:358–375
Saitô H, Ohki T, Takasuka N et al (1977) A 13C-N.M.R.-Spectral study of a gel-forming, branched (1 → 3)-β-d-glucan, (lentinan) from Lentinus edodes, and its acid-degraded fractions. Structure, and dependence of conformation on the molecular weight. Carbohyd Res 58:293–305
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP et al (2002) Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med 346:92–98
Shang S, Huang J (2009) Observation on short-term therapeutic and adverse effect of lentinan and vinorelbine and oxaliplatin in recombination on patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Focus 24:501–504
Shi X, Ding Q, Yang Q (2007) Lentinan combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. China Cancer 16:946–948
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG et al (1987) Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science (New York, NY) 235:177–182
Song Q, Zhu J (2016) Effect of Mushroom polysaccharide injection on serum tumor markers and clinical effect in patients with stage III and IV SCLC. J China Prescr Drug 14:12–13
Surenjav U, Zhang L, Xu X et al (2006) Effects of molecular structure on antitumor activities of (1 → 3)-β-d-glucans from different Lentinus edodes. Carbohyd Polym 63:97–104
The Top 10 Causes of Death (2018). http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/. Accessed 23 July 2018
Thomas AA, Brennan CW, DeAngelis LM et al (2014) Emerging therapies for glioblastoma. JAMA Neurol 71:1437–1444
van Meir H, Nout RA, Welters MJ et al (2017) Impact of (chemo)radiotherapy on immune cell composition and function in cervical cancer patients. Oncoimmunology 6:e1267095
Wang J (1994) Clinical observation of lentinan in treatment of 60 cases of hepatitis B. J Chin Med 16:23–24
Wang W, Dai X, Ouyang X (2006) Efficacy of lentinan combined with chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. China J Lung Cancer 09:78–81
Wang G, Lin W, Zhao R et al (2008) Effects of six polysaccharides extracted from plants on the immunological cells of mice. J Hyg Res 37:577–580
Wang J, Dong S, Liu C et al (2010) β-Glucan oligosaccharide enhances CD8(+) T cells immune response induced by a DNA vaccine encoding hepatitis B virus core antigen. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:645213
Wang J, Zhang Y, Zhao H (2011) The influence of immune functions and therapeutic and adverse effect of lentinan combined with chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Natl Med Front China 06:15–17
Wang JL, Bi Z, Zou JW et al (2012) Combination therapy with lentinan improves outcomes in patients with esophageal carcinoma. Mol Med Rep 5:745–748
Wang Y, Han X, Li YD et al (2015) Effects of tumor-specific antigen induced by lentinan on murine H22 hepatocellular carcinoma immunoprophylaxis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19:4516–4524
Wang P, Zhao S, Yang B et al (2016) Anti-diabetic polysaccharides from natural sources: a review. Carbohyd Polym 148:86–97
Wei Y, Xie M (2015) The influence of lentinan injection on curative effect and quality life of patients with medium and advanced lung cancer after chemotherapy. Guiding J Tradit Chin Med Pharm 21:25–27
Wu X (2009) Clinical observation on advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the old treated with lentinan combined with NVB and DDP. China Foreign Med Treat 28:76–77
Wu X (2015) Clinical analysis of lentinan combined with chemotherapy in treatment of advanced lung cancer. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med 27:456–458
Wu B, Zhang Y, Zhang L (1993) III clinical trial summary of lentinan in the treatment of 108 cases with chronic viral hepatitis. Fujian J Tradit Chin Med 24:10–13, 50
Xiao X, Liu C, Yuan X et al (2015) Clinical effect of lentinan combined with DP chemotherapy on middle-late stage non-small cell lung cancer. Pract J Card Cereb Pneumal Vasc Dis 23:91–93
Xie Z, Xie J, Wen J et al (2006) A comparison between TP regimen with lentinan and with megestrol acetate for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. China Cancer 15:199–202
Xin W, Shi L, Zhou Y (2016) Efficacy of lentinan combined with NP chemotherapy in treatment of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and its effect on immunologic function. Mod J Integr Tradit Chin West Med 25:3349–3351
Xu X, Pan C, Zhang L et al (2011) Immunomodulatory beta-glucan from Lentinus edodes activates mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB in murine RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Biol Chem 286:31194–31198
Yin H, Yang G (2016) Efficacy of synergistic combination of lentinan and GP regimen in stage IV lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Prog 14:687–689
Yoshino S, Tabata T, Hazama S et al (2000) Immunoregulatory effects of the antitumor polysaccharide lentinan on Th1/Th2 balance in patients with digestive cancers. Anticancer Res 20:4707–4711
Yoshino S, Yoshida S, Maeda N et al (2010) Clinical evaluation of the combination treatment of intrapleural or intraperitoneal administration of lentinan and OK-432 for malignant effusion. Gan to kagaku ryoho. Cancer Chemother 37:2798–2800
Yue F, Jia T (2010) Clinical observation of lentinan combined with paclitaxel liposome on advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Pract J Card Cereb Pneumal Vasc Dis 18:1791–1792
Zhang H (2016) Clinical analysis of lentinan combined with chemotherapy for elderly patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Shenzhen J Integr Tradit Chin West Med 26:44–45
Zhang H, Xu J, Ren S (2009) Lentinan combined with chemotherapy in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Cancer Biother 16:523–525
Zhang C, Xie C, Kang Z et al (2014) Clinical observation on GP chemotherapy combined with lentinan to treat metaphase or terminal non-small cell lung cancer. J Qiqihar Univ Med 35:164–165
Zhang Y, Li Q, Shu Y et al (2015a) Induction of apoptosis in S180 tumour bearing mice by polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes via mitochondria apoptotic pathway. J Funct Foods 15:151–159
Zhang Y, Yu J, Xiang Y et al (2015b) Clinical efficacy and safety of lentinan combined with chemotherapy for elderly patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Antitumor Pharm 03:222–225
Zhao L (2012) A clinical study on non-small cell lung cancer therapy by combination of lentinan with chemotherapy. Anhui Med Pharm J 16:1496–1497
Zhao X, Ma L (2011) Toxicity-reducing and efficacy-enhancing action of lentinan with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Ration Drug Use 04:20–21
Zhao C, Li X, Wang Z et al (2011) Immune function and effect of concurrent chemoradiotherapy combined lentinan on patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Anhui Med Pharm J 15:1431–1433
Zhao W, Chen D, Chen J (2013) Curative effect and adverse reaction of lentinan combined with gemcitabine and cisplatin in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther 18:71–77
Zheng H, Zeltsman M, Zauderer MG et al (2017) Chemotherapy-induced immunomodulation in non-small-cell lung cancer: a rationale for combination chemoimmunotherapy. Immunotherapy 9:913–927
Zhou C, Liu M (2010) 30 cases of adverse reaction caused by lentinan. Zhejiang J Integr Tradit Chin West Med 20:635
Zhou Z, Han Z, Zeng Y et al (2014) Chinese FDA approved fungal glycan-based drugs: an overview of structures, mechanisms and clinical related studies. Transl Med 04:1000141
Zhu Y, Zhang L (2013) Short-term curative effect of lentinan combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of lung cancer and its evaluation of immune function. China Pract Med 08:156–157
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Alexander Lu of St. Louis University for language editing of the entire manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 91129706, 81672585); Key Technology Fund of Shandong Province (Grant 2016ZDJS07A07); the “Double First-Class” fund of Shandong Province; Taishan Scholar Fellowship (05052011) and Postdoctoral application research project in Qingdao, China (Grant 40518060042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, M., Jiang, Y. et al. Lentinan as an immunotherapeutic for treating lung cancer: a review of 12 years clinical studies in China. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144, 2177–2186 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2718-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2718-1